Vin Diesel owns the Fredonia Barber Shop. He employs four barbers and pays each a base rate of $1,250 per month. One of the barbers serves as the manager and receives an extra $500 per month. In addition to the base rate, each barber also receives a commission of $4.50 per haircut.
Other costs are as follows
| Advertising | $200 per month |
| Rent | $1,100 per month |
| Barber supplies | $0.30 per haircut |
| Utilities | $175 per month plus $0.20 per haircut |
| Magazines | $25 per month |
Vin currently charges $10 per haircut
Instructions
- Determine the variable costs per haircut and the total monthly fixed costs.
- Compute the break-even point in units and dollars.
- Prepare a CVP graph, assuming a maximum of 1,800 haircuts in a month. Use increments of 300 haircuts on the horizontal axis and $3,000 on the vertical axis.
- Determine net income, assuming 1,600 haircuts are given in a month.
| Sales | $1,800,000 | Selling expenses-variable | $70,000 |
| Direct materials | 430,000 | Selling expenses-fixed | 65,000 |
| Direct labor | 360,000 | Administrative expenses-variable | 20,000 |
| Manufacturing overhead-variable | 380,000 | Administrative expenses-fixed | 60,000 |
| Manufacturing overhead-fixed | 280,000 |
Instructions
- Prepare a CVP income statement for 2023 based on management's estimates. (Show column for total amounts only)
- Compute the break-even point in (1) units and (2) dollars.
- Compute the contribution margin ratio and the margin of safety ratio. (Round to nearest full percent.).
- Determine the sales dollars required to earn net income of $180,000.
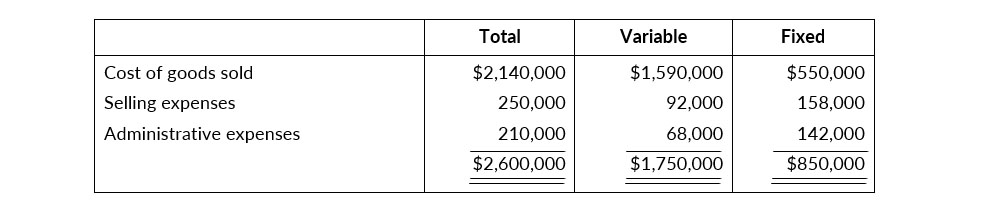
Management is considering the following independent alternative for 2021.
- Increase unit selling price 20% with no change in costs, expenses, and sales volume.
- Change the compensation of salespersons from fixed annual salaries totaling $150,000 to total salaries of $60,000 plus a 5% commission on sales
Instructions
- Compute the current break-even point in dollars for 2020
- Compute the break-even point in dollars under each of the alternative courses of action. (Round all ratios to nearest full percent.) Which course of action do you recommend?
Instructions
- Compute the current break-even point in units, and compare it to the break-even point in units if Mary's ideas area used.
- Compute the margin of safety ratio for current operations and after Mary's changes introduced. (Round to nearest full percent.)
- Prepare a CVP income statement for current operations and after Mary's changes are introduced (Show column for total amounts only.) Would you make use changes suggested
Instructions
- Compute (1) the contribution margin for the current year and the projected year, and (2) the fixed costs for the current year. (Assume that fixed costs will remain the same in the projected year.
- Compute the break-even point in units, and sales dollars for the current year.
- The company has a target net income of $200,000. What is the required sales in dollars for the company to meet its target?
- If the company meets its target net income number, by what percentage could its sales fall before it is operating at a loss? That is, what is its margin of safety ratio?
The controller of Norton Industries has collected the following monthly expense data for use in analyzing the cost behavior of maintenance costs.
| Month | Total Maintenance Costs | Total Machine Hours |
| January | $2,700 | 300 |
| February | 3,000 | 350 |
| March | 3,600 | 500 |
| April | 4,500 | 690 |
| May | 3,200 | 400 |
| June | 5,500 | 700 |
Instructions
- Determine the fixed and variable cost components using the high-low method.
- Prepare a graph showing the behavior of maintenance costs, and identify the fixed and variable cost elements. Use 100-hour increments and $1,000 cost increments
- Wood used in the production of furniture.
- Fuel used in delivery trucks.
- Straight-line depreciation on factory building.
- Screws used in the production of furniture.
- Sales staff salaries.
- Sales commissions.
- Property taxes.
- Insurance on buildings.
- Hourly wages of furniture craftsmen
- Salaries of factory supervisors.
- Utilities expense.
- Telephone bill
Instructions
Identify the costs above as variable, fixed, or mixed.
Instructions
-------- Prepare a memo to Marty Moser concerning the assumptions that underline CVP analysis.


